ReactJS Interview Questions
1. What is ReactJS?
React is an open-source, front end, component-based JavaScript library for building user interfaces or UI components of websites and mobile applications. It is developed by Facebook in 2011, Maintained by Facebook and a community of individual developers and companies. React can be used as a base in the development of single-page or mobile applications. Currently, it is one of the most popular front-end JavaScript library in the industry.
2. What are the features of ReactJS?
Features are:
3. What are the limitations of ReactJS?
4. What is JSX?
JSX stands for JavaScript XML. It allows us to write HTML inside JavaScript and place them in the DOM without using functions like appendChild( ) or createElement( ) Consider this variable declaration: const name = 'Josh Perez'; const element = <h1>Hello, {name}</h1>; ReactDOM.render( element, document.getElementById('root') ); The above tag syntax is neither a string nor HTML. It is called JSX, and it is a syntax extension to JavaScript. We recommend using it with React to describe what the UI should look like. JSX may remind you of a template language, but it comes with the full power of JavaScript. JSX produces React “elements”.
5. Differentiate between Real DOM and Virtual DOM.
Real DOM
Virtual DOM
When anything needed to update on DOM, Real DOM updates slowly
Virtual DOM is faster than Real DOM
It directly updates the HTML.
It does not directly update HTML.
Creates a new DOM if element updates.
Updates the JSX if element updates.
memory wastage is more.
No memory wastage.
6. What are the different phases of React component’s lifecycle?
There are four different phases of React component’s lifecycle: Initial Rendering Phase: This is the phase when the component is about to start its life journey and make its way to the DOM. Updating Phase: Once the component gets added to the DOM, it can potentially update and re-render only when a prop or state change occurs. That happens only in this phase. mounting Phase: In this phase component is mounted Unmounting Phase: This is the final phase of a component’s life cycle in which the component is destroyed and removed from the DOM.
7. Explain the purpose of render() in React.
Render function is part of the react component lifecyle where ReactDOM is the class object which exposes a method called render which is used to render the React JSX content into your DOM.
8. What is the state in React and how is it used?
States are the heart of React components. States are the source of data and must be kept as simple as possible. Basically, states are the objects which determine components rendering and behavior. They are mutable unlike the props and create dynamic and interactive components. They are accessed via this.state(). 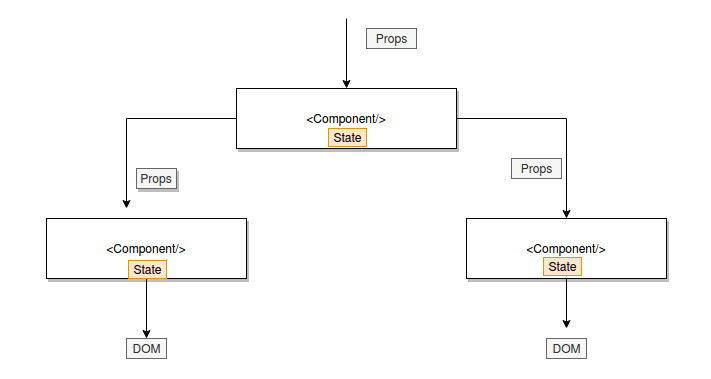
9. How is React different from Angular?
TOPIC
REACT
ANGULAR
ARCHITECTURE
It is only the View part of MVC
Complete MVC
RENDERING
It supports Server side rendering
By defaut it does Client side rendering
DOM
It uses virtual DOM
It uses real DOM
DATA BINDING
One-way data binding
Two-way data binding
DEBUGGING
Compile time debugging
Run time debugging
AUTHOR
Facebook
Google
10. What are props?
As Per React's Thinking in React documentation, props are best explained as "a way of passing data from parent to child." That's it. In essence, props are just a communication channel between components, always moving from top (parent) to bottom (child).
11. Differentiate states and props.
Conditions
State
Props
Receive initial value from parent component
Yes
Yes
Parent component can change value
No
Yes
Set default values inside component
Yes
Yes
Changes inside component
Yes
No
Set initial value for child components
Yes
Yes
Changes inside child components
No
Yes
12. Differentiate between stateful and stateless components.
Stateful Component
Stateless Component
Stores info about component’s state change in memory
Stores info about component’s state change in memory
Have authority to change state
Do not have the authority to change state
Contains the knowledge of past, current and possible future changes in state
Contains no knowledge of past, current and possible future state changes
Stateless components notify them about the requirement of the state change, then they send down the props to them.
They receive the props from the Stateful components and treat them as callback functions.
13. What is an event in React?
In React, events are the triggered reactions to specific actions like mouse hover, mouse click, key press, etc. Handling these events are similar to handling events in DOM elements. But there are some syntactical differences like: Events are named using camel case instead of just using the lowercase. Events are passed as functions instead of strings. The event argument contains a set of properties, which are specific to an event. Each event type contains its own properties and behavior which can be accessed via its event handler only.
14. What are Higher Order Components(HOC)?
Higher Order Component is an advanced way of reusing the component logic. Basically, it’s a pattern that is derived from React’s compositional nature. HOC are custom components which wraps another component within it. They can accept any dynamically provided child component but they won’t modify or copy any behavior from their input components. You can say that HOC are ‘pure’ components.
15. What are Pure Components?
Pure components are the simplest and fastest components which can be written. They can replace any component which only has a render(). These components enhance the simplicity of the code and performance of the application.
16. What is the significance of keys in React?
Keys are used for identifying unique Virtual DOM Elements with their corresponding data driving the UI. They help React to optimize the rendering by recycling all the existing elements in the DOM. These keys must be a unique number or string, using which React just reorders the elements instead of re-rendering them. This leads to increase in application’s performance.
17. What were the major problems with MVC framework?
Following are some of the major problems with MVC framework:
18. What is Redux?
Redux is one of the hottest libraries for front end development in today’s marketplace. It is a predictable state container for JavaScript applications and is used for the entire applications state management. Applications developed with Redux are easy to test and can run in different environments showing consistent behavior.
19. What do you understand by “Single source of truth”?
Redux uses ‘Store’ for storing the application’s entire state at one place. So all the component’s state are stored in the Store and they receive updates from the Store itself. The single state tree makes it easier to keep track of changes over time and debug or inspect the application.
20. List down the components of Redux.
Redux is composed of the following components: Action – It’s an object that describes what happened. Reducer – It is a place to determine how the state will change. Store – State/ Object tree of the entire application is saved in the Store. View – Simply displays the data provided by the Store. 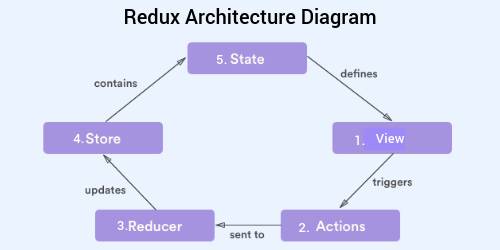
21. Explain the role of Reducer.
Reducers are pure functions which specify how the application’s state changes in response to an ACTION. Reducers work by taking in the previous state and action, and then it returns a new state. It determines what sort of update needs to be done based on the type of the action, and then returns new values. It returns the previous state as it is, if no work needs to be done.
22. What is the significance of Store in Redux?
A store is a JavaScript object which can hold the application’s state and provide a few helper methods to access the state, dispatch actions and register listeners. The entire state/ object tree of an application is saved in a single store. As a result of this, Redux is very simple and predictable. We can pass middleware to the store to handle processing of data as well as to keep a log of various actions that change the state of stores. All the actions return a new state via reducers.
23. How is Redux different from Flux?
State is immutable
Flux
Redux
The Store contains state and change logic
Store and change logic are separate
There are multiple stores
There is only one store
All the stores are disconnected and flat
Single store with hierarchical reducers
Has singleton dispatcher
No concept of dispatcher
React components subscribe to the store
Container components utilize connect
State is mutable
24. What is the virtual DOM?
A virtual DOM object is a representation of a REAL DOM object, like a lightweight copy. A virtual DOM object has the same properties as a real DOM object, but it lacks the real thing’s power to directly change what’s on the screen. Manipulating the DOM is slow. Manipulating the virtual DOM is much faster, because nothing gets drawn onscreen. Think of manipulating the virtual DOM as editing a blueprint, as opposed to moving rooms in an actual house.
25. How event can be created in React?
<button onClick="showAlert()">Show Alert</button>
26. Show list item can be rendered in ReactJS?
Most common way to render list item in ReactJS application is using map function. See below:
27. What is the reason of using keys in rendering list items?
28. What are the differences between state and props?
State
Props
State is mutable.
Props are immutable.
Stateless components cannot have State.
Stateless component can have Props.
State cannot make components reusable.
Props make components reusable.
State cannot be accessed by child components.
Props can be accessed by the child component.
State holds information about the components.
Props allow you to pass data from one component to other components as an argument.
29. What is the Flux?
Flux is the application architecture that Facebook uses for building client-side web applications. It is a method of handling complex data inside a client-side application and manages how data flows in a React application.
30. List some of the cases when you should use Refs.
31. What is difference between Redux and Flux?
Redux
Flux
It open-source JavaScript library used to manage application State
It is an architecture and not a framework or library
It uses the concept of reducer
It uses the concept of the dispatcher
Store’s state is immutable
Store’s state is mutable
Only have a single-store
It have multiple stores
32. What is React Router?
React Router is a routing library used to create routes in a React application.
33. What are the ways to create components in React?
Component is created in React.js using two ways: 1. Function Components: This is the easiest way to create a component in ReactJS. Those are pure JavaScript functions that accept props object as first parameter and return React elements: function GreetUser({ message }) { return <h1>{`Hey , ${message}`}</h1> } 2. Class Components: You can also use ES6 class to define a component. The above function component can be written as: class Greeting extends React.Component { render() { return <h1>{`Hello, ${this.props.message}`}</h1> } }
34. What is the use of refs?
It is used to return a reference to the element. It is avoided in most cases, but can be useful when you need a direct access to the DOM element or an instance of a component.
35. What is the difference between Shadow DOM and Virtual DOM?
The Shadow DOM is a browser technology designed primarily for scoping variables and CSS in web components. The Virtual DOM is a concept implemented by libraries in JavaScript on top of browser APIs.
36. What is context API?
Context provides a way to pass data through the component tree without having to pass props down manually at every level. For example, authenticated user, locale preference, UI theme need to be accessed in the application by many components. const {Provider, Consumer} = React.createContext(defaultValue)
37. How to write comments in React?
Single-line comments: <div> {/* Single-line comments(In vanilla JavaScript, the single-line comments are represented by double slash(//)) */} </div> Multiple line comments: <div> {/* Multi-line comments, this is line 1 This is line 2*/} {`Hey ${user}, Welcome to this app`} </div>
38. What is reconciliation?
When a component's props or state change, React decides whether an actual DOM update is necessary by comparing the newly returned element with the previously rendered one. When they are not equal, React will update the DOM. This process is called reconciliation.
39. Why className not class attribute in ReactJS?
class is a keyword in javascript and JSX is an extension of javascript. That is the main reason due to which React uses className instead of class.
40. What are portals in React?
Portal is a recommended way to render children into a DOM node that exists outside the DOM hierarchy of the parent component. ReactDOM.createPortal(child, container)
41. What is difference between Library and Framework?
React is a library and Angular is a framework. In simple terms, a library solves single problem, whereas a framework solves a group of problems. Most often, frameworks consist of libraries
42. What is React Fiber?
React Fiber is a set of internal algorithms for rendering graphics used by the JavaScript library React, as opposed to its old rendering algorithm, Stack.
43. What is the main goal of React Fiber?
The goal of React Fiber is to increase its suitability for areas like animation, layout, and gestures. Its headline feature is incremental rendering: the ability to split rendering work into chunks and spread it out over multiple frames.
44. What is the difference between createElement and cloneElement?
JSX elements will be transpiled to React.createElement() functions to create React elements which are going to be used for the object representation of UI. Whereas cloneElement is used to clone an element and pass it new props.
45. What are React Fragments?
Fragments are a modern syntax for adding multiple elements to a React Component without wrapping them in an extra DOM node. render() { return ( <React.Fragment> <ChildComponentA /> <ChildComponentB /> <ChildComponentC /> </React.Fragment> ) }