TypeScript Promises Examples
The popularity of TypeScript is increasing very rapidly for frontend web development as well as backend web development. TypeScript is designed for the development of large applications and transpiles to JavaScript. As TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript, existing JavaScript programs are also valid TypeScript programs. TypeScript may be used to develop JavaScript applications for both client-side and server-side execution. If you are completely new to TypeScript for serverside(Node.js) then read this article to get the basic understanding of Typescript and how it can be used with Node.js
In this article, We will understand about promises in TypeScript and how we can make our code efficient after using promise in our TypeScript Code.
Callback examples in TypeScript
One way to program asynchronously is to use callbacks. We pass to an asynchronous function a function which it will call when the task is completed.
Let's understand with below example:
In the example above, A normal function is defined and an argument is passed which is a function and will be called once the task inside the function block is completed.
Start Working with Promises
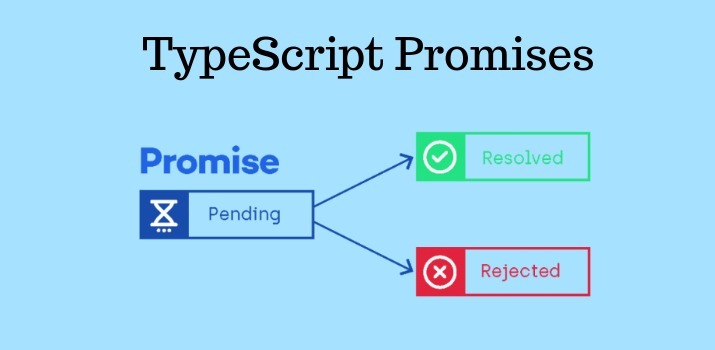
A promise is an object that may produce a single value sometime in the future: either a resolved value or a reason that it’s not resolved (e.g., a network error occurred). A promise may be in one of 3 possible states: fulfilled, rejected, or pending. Promise users can attach callbacks to handle the fulfilled value or the reason for rejection.
State of Promises
- pending: This is the initial state which indicates that promise has not either resolved or rejected. For example, We are making any HTTP call and the request takes few milliseconds to get response, so while its waiting for the response the state of the promise will be in pending state.
- fulfilled: This is the state which indicates that the final output has been returned by promise successfully.
- rejected: This state denotes that some error has been occured while doing task inside the promises and the operation gets failed.
- In example above, a promise takes callback function as a parameter.
- Its callback function has 2 parameters resolve and reject.
- If the condition inside promise is true then the promise returns resolve else it returns the reject.
Inside the coding a promise condition is writen like below to return a valid promise.
Attach Success and Error Handler with Promise
A function returning promise can be handled easily like in below code:
Promise Chaining
We can also connect a series of then handlers together in a chain, like in below example:
Conclusion
The promise is a very efficient way to write asynchronous code. Also, it solved all the problem occurred while working with callbacks.
Thank You!
Find other similar Articles here:
- JavaScript or Python which is better for the future?
- What are the Different Approaches to Encrypt Data before Storing in Databse
- What is difference between Promise and Async await in javascript
- What is difference between monolithic architecture and microservices architecture
- Difference between for loop and forEach in Javascript
- Different ways to convert string to number in JavaScript