Getting Started with Git

GIT is a distributed version control system and source code management system with an emphasis to handle small and large projects with speed and efficiency. It is one of the very important tool for a developer these days. For sharing project to other developers, or to start a big project by multiple people, Git plays a very major role to manage the code in that situation. For version control there are also other tools like SVN, CVS, Mercurial but Git is very popular among developers.
Git Basics to start with
There are some predefined commands to manage everything while using git.
- git init - The git init command creates a new Git repository. It is used to convert an existing, unversioned project to a Git repository or initialize a new, empty repository. Most other Git commands are not available outside of an initialized repository, so this is usually the first command you'll run in a new project.
- git status - This command displays the state of the working directory and the staging area.
- git add - This command set the state of a file from untracked or modified to staged.
- git commit - ?Grab the currently staged files and create a log describing the change made in those files.
- git push?—?This command sends everything you committed to the server remotely.
- git fetch? - ?Fetches references of branches remotely.
- git pull - Get new commits for the current branch that are available remotely.
- git checkout - ?Get the branch from the remote server.
- git reset? -? This command revert a commit you did by mistake.
File status
While working with git below are the various status that files can have:
Untracked?—?A file that was never versioned by git. You can stage it for a commit using git add [file] or git add . to add all the untracked and modified files;
Tracked?—?Files that are being tracked by git, when a change happen you will see it in git status has modified;
Modified?—?When a versioned file is changed;
Staged —When you add a file or files to be committed with the same commit message. This usually happens after a git add command.
Committed?—?When you commit something it means it is ready to be sent to your remote repository, files that are in this state can be listed with git log(it will also show the rest of the commit history of the repository)
Remote?—?To send something to the remote repository you have to do git push else anybody else working on your project won’t see your changes, up until the “committed” point all the files are on your machine only.
Tools
There is also GUI tools available to help developers visualize the working process. It is very helpful is one is not confortable with terminal approach
- Source tree (free)
- Github desktop (free)
- Git Tower (paid)
- Git Kraken (paid)
Advantages of using Git
Feature Branch Workflow
One of the biggest advantages of Git is its branching capabilities. Unlike centralized version control systems, Git branches are cheap and easy to merge. This facilitates the feature branch workflow popular with many Git users.
Distributed Development
It provides a distributed version control system. Instead of a working copy, each developer gets their own local repository, complete with a full history of commits.
Pull Requests
A pull request is a way to ask another developer to merge one of your branches into their repository.
Faster Release Cycle
The ultimate result of feature branches, distributed development, pull requests, and a stable community is a faster release cycle.
Disadvantages of using Git
There are very few disadvantages of using GIT:
- Git is less preferred for handling extremely large files or frequently changing binary files .
- GIT does not support ‘commits’ across multiple branches or tags.
Github example
Step 1: Create a new repository
If you don't have account over github then create an account on github and create a repository by pressing the “+” in the upper right corner near profle image.
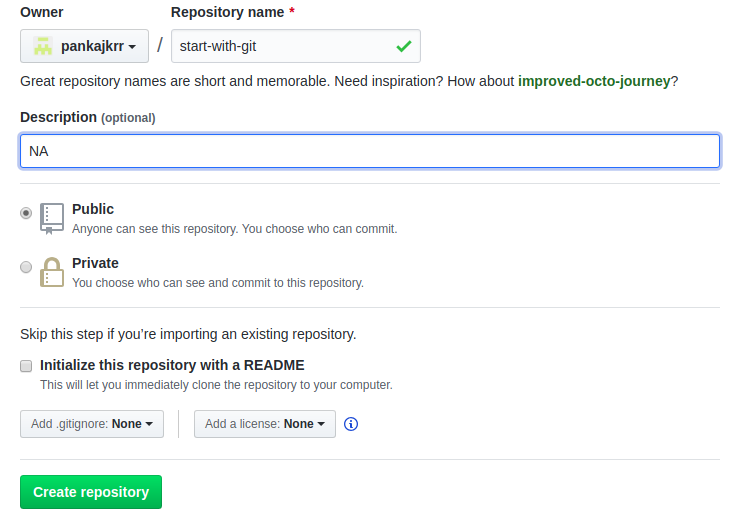
After clicking over the Create repository button above a new page will open over github like below:
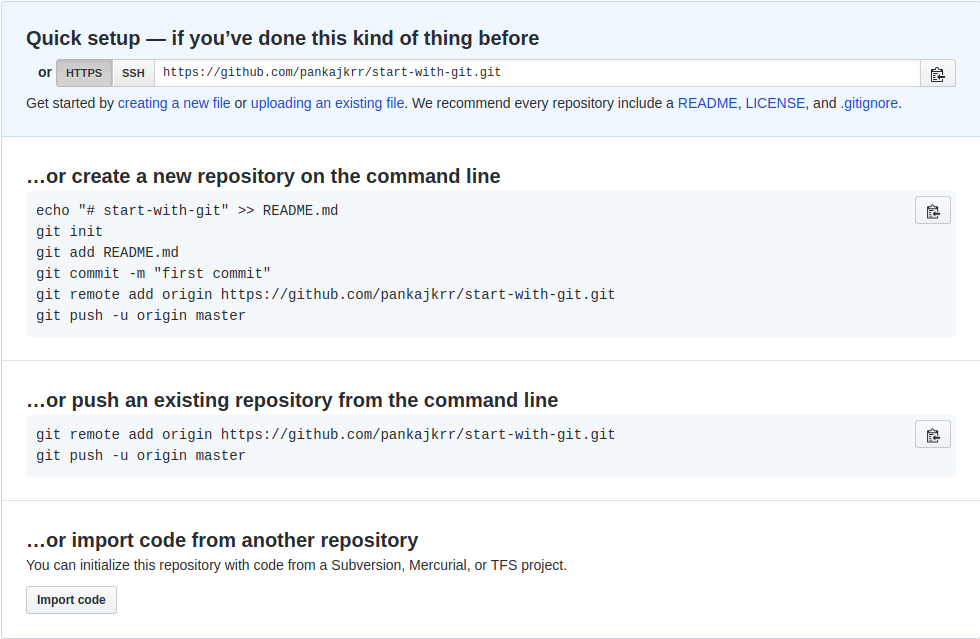
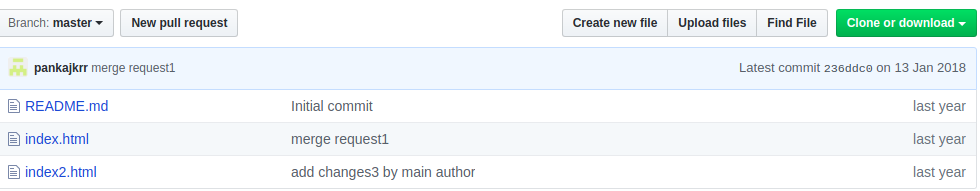
In the above image you can see there are two option to push the code over git. First, to create a new repository and other to push an existing code. For now you have to choose the first one. After pushing all the code over git, you will be able to see your file under the repository like below:
Conclusion
In this article, We tried to understand the topic 'Getting Started with Git'. This will give you an idea an a base to get you started, everything in this process can and should be refined as you learn more about the topic.
Let me know your thoughts over the email demo.jsonworld@gmail.com. I would love to hear them and If you like this article, share with your friends.
Find other similar Articles here:
- JavaScript or Python which is better for the future?
- What are the Different Approaches to Encrypt Data before Storing in Databse
- What is difference between Promise and Async await in javascript
- What is difference between monolithic architecture and microservices architecture
- Difference between for loop and forEach in Javascript
- Different ways to convert string to number in JavaScript